
The vision of onchain lending protocols - a cornerstone of Internet Finance - is to provide equal access to capital for individuals and businesses, regardless of location. Doing so enables fairer and more efficient capital markets, ultimately increasing economic growth.
Despite its potential, onchain lending today primarily caters to crypto-natives and provides little utility outside speculative use cases. This significantly constrains the total addressable market (TAM).
This post explores how to expand the user base and transition to more productive use cases in a step-by-step approach while navigating potential challenges.
Onchain Lending Today
In just a few years, the onchain lending market has grown from an early concept to numerous battle-tested protocols that have withstood several high-volatility events without incurring bad debt. In total, these protocols have amassed $43.7 billion in deposits and $18.6 billion in outstanding loans.
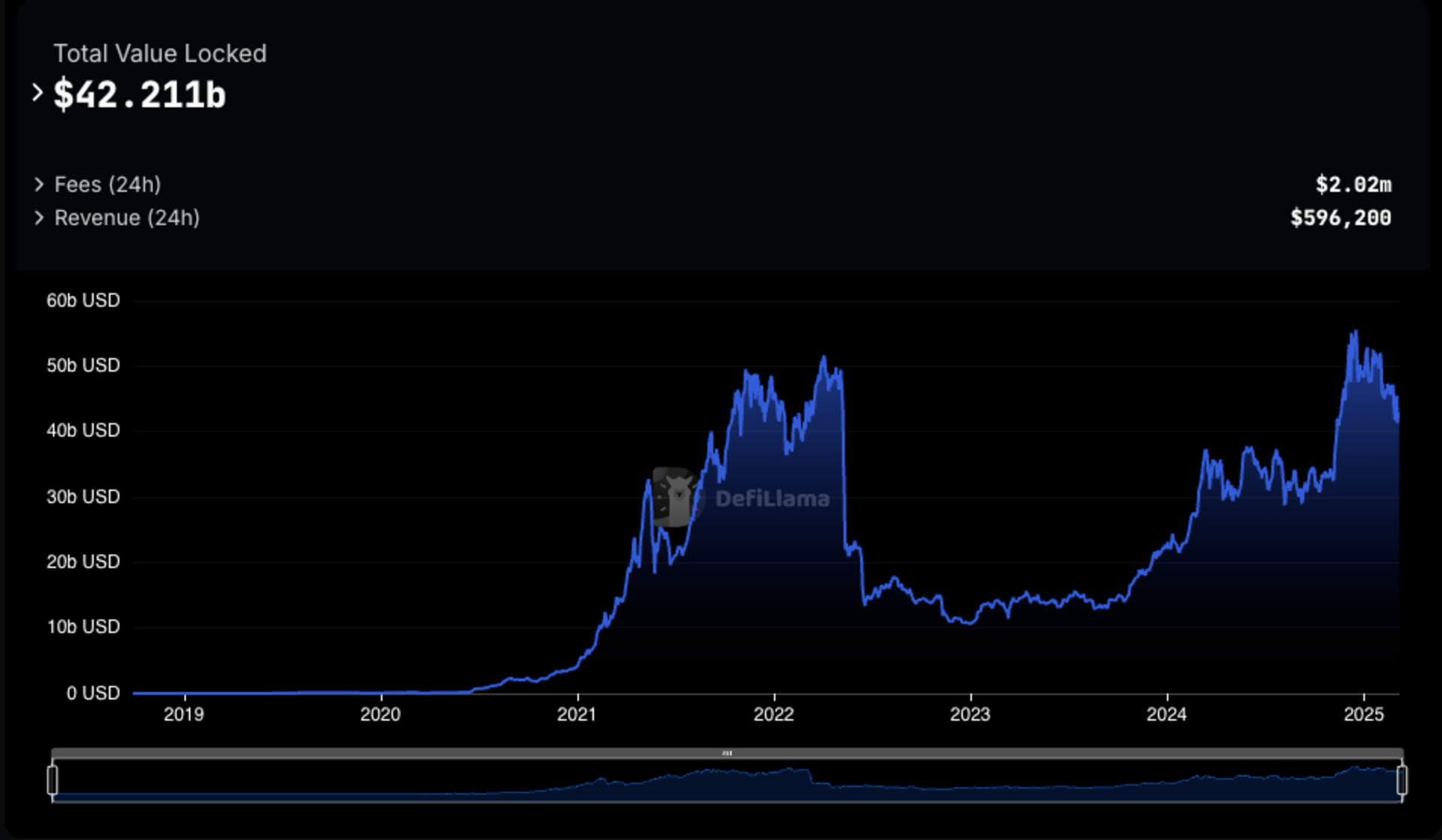
Source: DefiLlama
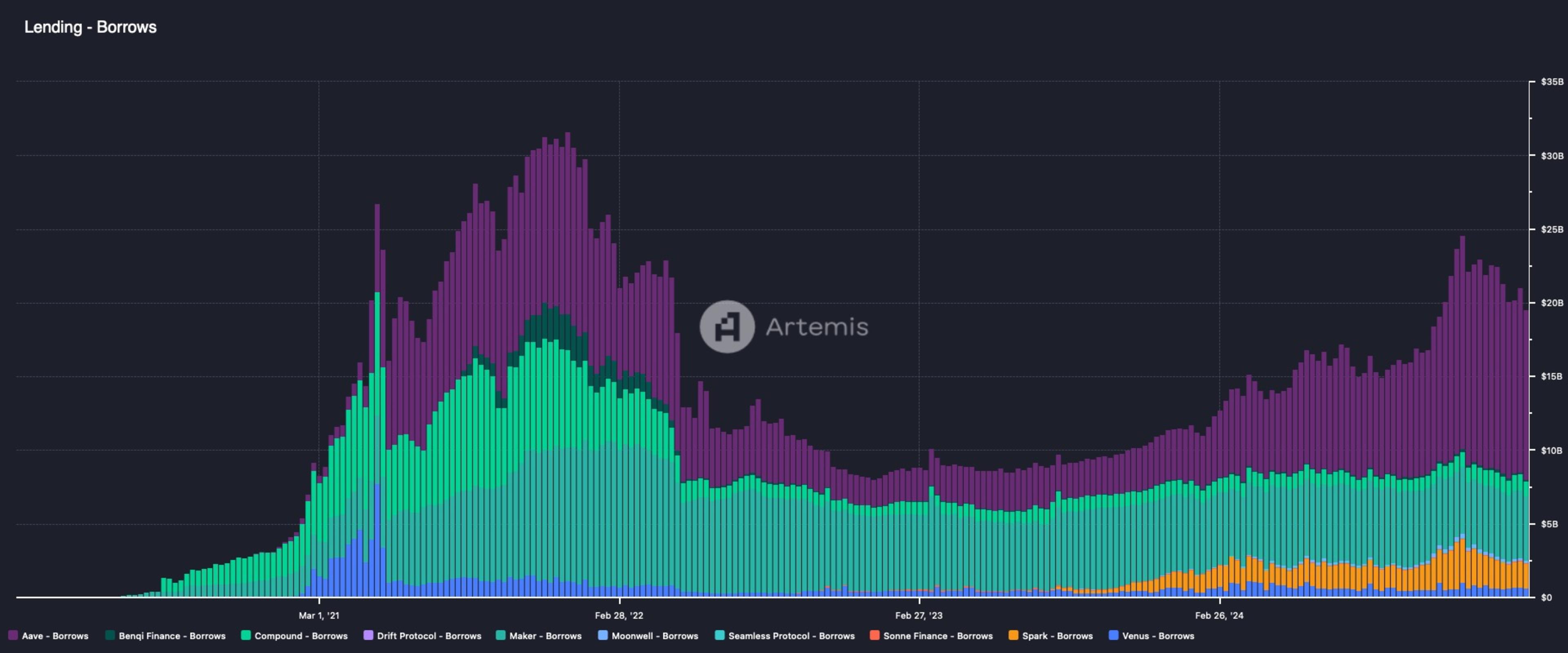
Source: Artemis
Today, the primary demand for onchain lending protocols comes from:
Speculation: Leverage for crypto native investors to buy more crypto (e.g., borrowing USDC against BTC to buy more BTC, potentially looping that position multiple times to increase leverage)
Accessing Liquidity: Enabling investors to get liquidity on their crypto holdings without selling and potentially incurring cap gains tax (depending on their jurisdiction).
Flash loans for arbitrageurs: A very short-term loan (repaid during the same block as it’s issued) used by arbitrageurs to exploit temporary market inefficiencies and correct mispricings.
All of these target crypto-natives and serve mainly speculative purposes. However, the vision for onchain lending is much larger.
When comparing the total amount of outstanding debt in the world ($320 trillion) or total loans to households and non-financial corporates ($120 trillion), the $18.6 bn that onchain lending protocols have in outstanding loans is merely a drop in the ocean.
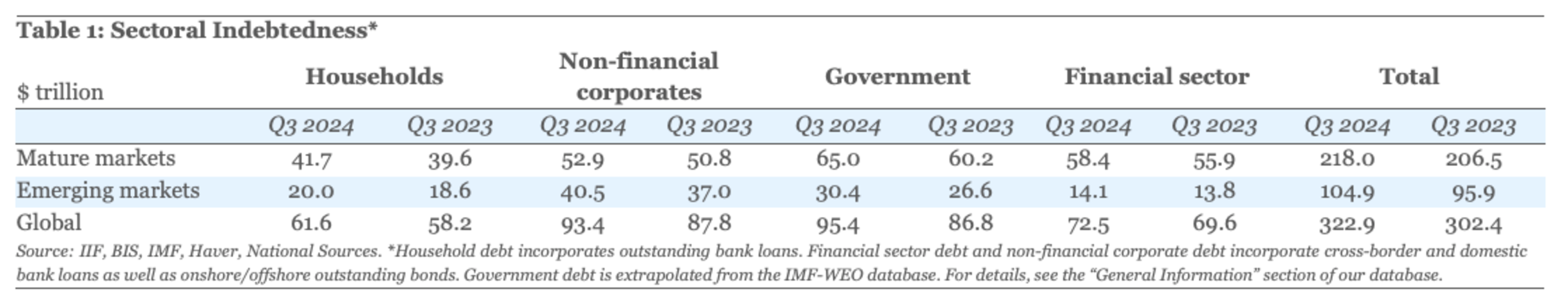
Source: IIF Global Debt Monitor
The TAM of onchain lending can increase several orders of magnitude as it moves towards more productive uses of capital (e.g., loans to finance small businesses or individuals buying a car or house).
Onchain Lending Tomorrow
Two significant changes are needed to increase the utility of onchain lending:
Broadening the collateral pool: Today, only select crypto assets can be used as collateral, which limits the pool of potential borrowers. In addition, the high collateral ratios (up to 2x or higher to compensate for the high volatility of crypto tokens) further limit borrowing demand. Expanding the pool of accepted collateral enables more investors to borrow against their portfolio of assets and onchain lending protocols to underwrite more loans.
Enabling undercollateralized lending: The vast majority of onchain lending protocols today are overcollateralized (borrowers put up more capital than they borrow), which makes borrowing capital-inefficient and unfeasible for many use cases (e.g., financing small businesses). By embracing undercollateralized loans, onchain lending can appeal to a broader range of borrowers.
Some of these features are easier to implement, while others introduce new challenges. However, implementation can happen in steps, starting with the low-hanging fruit.
Let’s examine each in more detail.
A third feature is fixed-rate lending, but this could be solved by a third party taking over the variable rate risk from the borrower through an interest rate swap or custom-lending agreements between borrowers and lenders, so we won’t cover it here (and some protocols, such as Notional, already offer this).
1. Broadening The Collateral Pool
Compared to other global assets such as public equities ($124 trillion), fixed income ($140 trillion), or real estate ($380 trillion), the market cap of crypto ($3 trillion) is only a fraction of that. Restricting the collateral pool to a subset of crypto tokens significantly limits the growth of onchain lending, particularly as collateral requirements can be up to 2x (or even higher) to compensate for the high volatility of crypto assets.
Combining tokenization with onchain lending enables investors to borrow against their total portfolio of assets more effectively (rather than just a small subset), widening the pool of potential borrowers.
The expansion of collateral is likely to begin with liquid, frequently traded assets (stocks, money-market funds, bonds, etc.), which would require limited changes to existing lending protocols. However, the speed of regulatory approval is a key factor restricting growth here.
In the longer term, expanding to more illiquid and physical assets (such as tokenized real estate ownership) offers an interest growth avenue but also brings unique challenges, such as managing the debt position.
Eventually, we could enable individuals to leverage onchain lending for mortgages where the loan issuance, purchase of the house, and depositing the house as collateral in a lending protocol happens atomically within one block. Similarly, a business could take out a loan to invest in a new plant or machinery by simultaneously depositing that asset as collateral.
2. Enabling Undercollateralized Lending
Today, the vast majority of onchain lending is overcollateralized, meaning borrowers must put up more capital than the amount they borrow. This approach, while ensuring the lender's security, is capital-inefficient and unfeasible for many use cases (e.g., working capital loans for capital-light businesses).
Initial demand for undercollateralized lending within crypto would likely come from market makers and other crypto-native institutions left unserved after the collapse of centralized lending desks (BlockFi, Genesis, Celsius, etc.). Meanwhile, early attempts to do undercollateralized lending in a more decentralized way, such as Goldfinch and Maple, either handle most of the logic off-chain or have pivoted to overcollateralized lending.
One interesting new entrant is Wildcat Finance, which aims to bring back undercollateralized lending while keeping more components onchain. It works merely as a matching engine between individual borrowers and lenders, leaving lenders to assess the underwriting risks.
Outside of the crypto-bubble, undercollateralized lending occurs among both consumers (e.g., personal loans, credit card debt, and BNPL) and commercial entities (e.g., loans for working capital, microfinance, trade finance, and business lines of credit).
The most significant opportunity for onchain lending products is within markets currently underserved by traditional banks. A couple of examples include:
In recent years, alternative lenders have increased their share in undercollateralized lending to consumers, particularly for low- and moderate-income households. Onchain lending can serve as a natural extension of this trend and provide more competitive rates for consumers by
Small businesses are finding it increasingly difficult to get loans (either for expanding operations or covering working capital) as big banks don’t deem it worthwhile due to small transaction amounts.
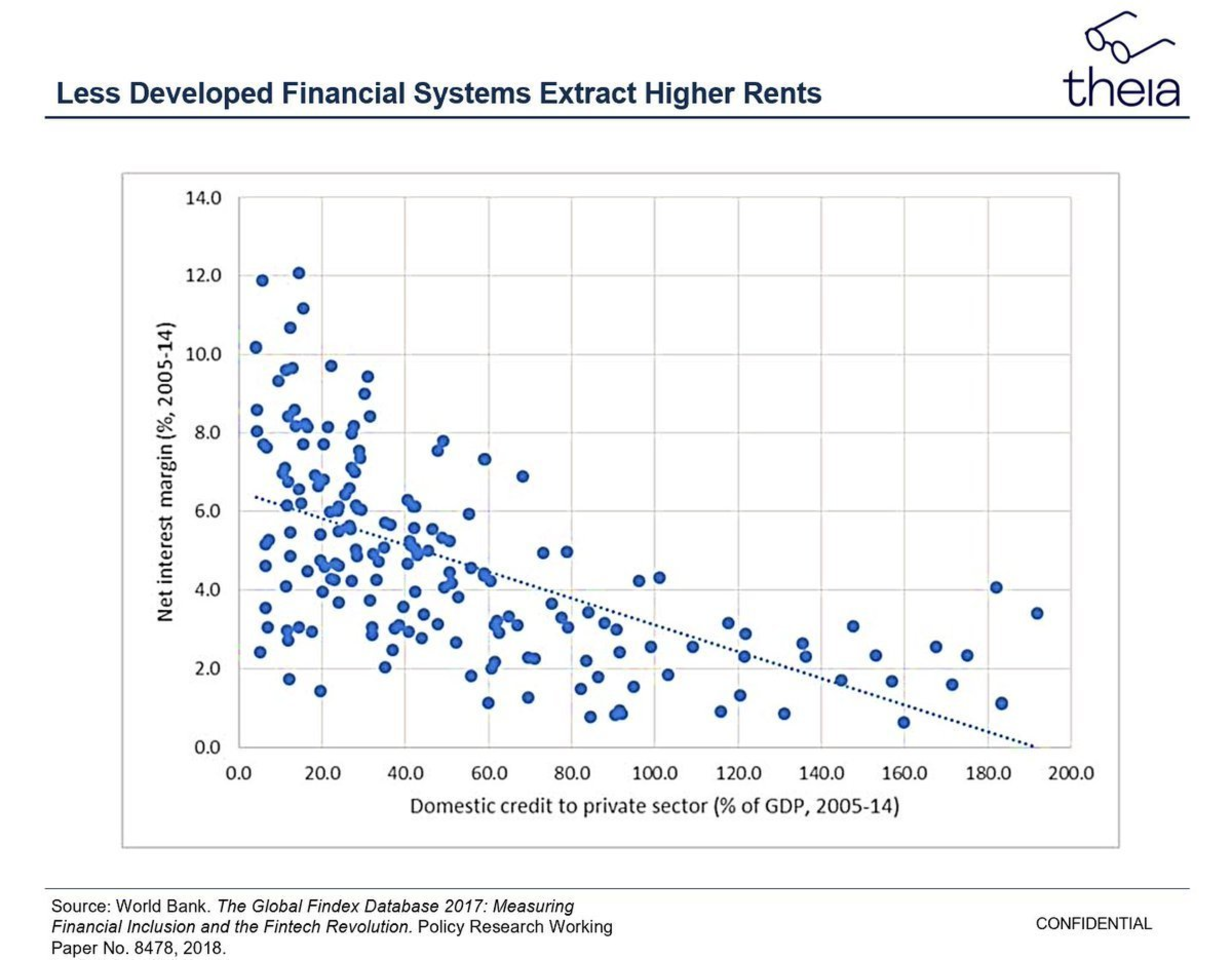
Onchain lending protocols can help reduce the cost of capital by minimizing the number of rent-seeking intermediaries and breaking oligopolistic pricing (Source)
Challenges To Overcome
While these two changes would expand the potential user base of onchain lending and enable more productive use cases, they also introduce new challenges. Some of these challenges include:
Managing debt positions backed by illiquid assets: While crypto trades 24/7 and many other liquid assets (public equity and debt) trade Monday through Friday, the prices of illiquid assets are updated much less frequently. Irregular price updates make managing the debt position more challenging, particularly in times of high volatility.
Liquidation of physical collateral: While the ownership of a physical asset may be represented on-chain, the liquidation process becomes more involved compared to assets that are fully onchain. With tokenized real estate, for example, the owner might refuse to leave the property without legal proceedings. Given that this falls outside the scope of an onchain lending protocol (and individual lenders), the liquidation right could be sold (at a discount) to a third-party debt collector in the local jurisdiction, who then handles the liquidation.
Determining the risk premium: While defaults are part of the lending business, the default risk should be incorporated in the risk premium (additional rate on top of the risk-free rate). Estimating default risk is primarily relevant for undercollateralized lending. While the required metrics to estimate this differ depending on the borrower, we already have tools to do this today:
Consumers: Web proofs, ZKPs, and decentralized identity protocols can help consumers prove their credit score, current income, employment status, and other personal data in a privacy-preserving way.
Companies: By integrating common accounting software and attested audit reports, companies can prove their cash flows, balance sheets, and more. In the future, if (or when) all finance eventually flows onchain, company data can be directly integrated into the lending protocol or 3rd party credit rating service in a more trust-minimized manner.
Decentralized credit risk model: Banks leverage internal customer data on top of externally available data to train their credit risk models, which help them determine underwriting risk. The data silos not only increases the barrier of entry as new entrants don’t have access to the same amount of data, but is also challenging to do in a decentralized manner (one entity doesn’t control the model, and data needs to be kept private). However, decentralized training and inference are improving quickly. In the future, decentralized protocols could leverage these methods to train a credit risk model and do inference in a privacy-preserving way.
Other challenges include onchain privacy, adapting risk parameters as the collateral pool expands, regulatory compliance, and making it easier to use borrowed proceeds for real-world utility.
Conclusion
While they’ve set a strong foundation over the last few years, onchain lending protocols have merely scratched the surface of their full potential.
The next phase of onchain lending is significantly more exciting. We expect protocols to expand slowly from crypto-native and speculative use cases to more productive ones.
In its final form, onchain lending helps level the playing field by providing companies and individuals equal access to capital, regardless of location. As Theia Research recently summarized:
The goal is a financial system where NIMs compress towards the cost of capital
That’s a north star worth fighting for!
If you are working on any of the problems mentioned in this post, we’d love to hear from you.
Continue reading

May 28, 2025
State of Verifiable Inference & Future Directions
Verifiable inference enables proving the correct model and weights were used, and that inputs/outputs were not tampered with. This post covers different approaches to achieve verifiable inference, teams working on this problem, and future directions.

March 25, 2025
Introducing Our Entrepreneur in Residence (EIR) Program
After 6+ years of building core blockchain infrastructure across most ecosystems and incubating ventures like ZkCloud, we're looking for ambitious pre-founders with whom to collaborate closely.

February 18, 2025
Can Blockchains And Cryptography Solve The Authenticity Challenge?
As gen-AI models improve, it's becoming increasingly difficult to differentiate between AI- and human-generated content. This piece dives into whether cryptography and blockchains can solve the authenticity challenge and help restore trust on the Internet

February 6, 2025
Vertical Integration for both Ethereum and ETH the Asset
In recent months, lackadaisical price action and usage growing on other L1/L2s has driven a discussion on what Ethereum’s role and the value of ETH, the asset is long-term.

January 29, 2025
Equilibrium: Building and Funding Core Infrastructure For The Decentralized Web
Combining Labs (our R&D studio) and Ventures (our early-stage venture fund) under one unified brand, Equilibrium, enables us to provide more comprehensive support to early-stage builders and double down on our core mission of building the decentralized web

November 28, 2024
20 Predictions For 2025
For the first time, we are publishing our annual predictions for what will happen by the end of next year and where the industry is headed. Joint work between the two arms of Equilibrium - Labs and Ventures.

November 7, 2024
9 + 1 Open Problems In The Privacy Space
In the third (and final) part of our privacy series, we explore nine open engineering problems in the blockchain privacy space in addition to touching on the social/regulatory challenges.

October 15, 2024
Aleo Mainnet Launch: Reflecting On The Journey So Far, Our Contributions And Path Ahead
Equilibrium started working with Aleo back in 2020 when ZKPs were still mostly a theoretical concept and programmable privacy in blockchains was in its infancy. Following Aleo's mainnet launch, we reflect on our journey and highlight key contributions.

August 12, 2024
Do All Roads Lead To MPC? Exploring The End-Game For Privacy Infrastructure
This post argues that the end-game for privacy infra falls back to the trust assumptions of MPC, if we want to avoid single points of failure. We explore the maturity of MPC & its trust assumptions, highlight alternative approaches, and compare tradeoffs.

June 12, 2024
What Do We Actually Mean When We Talk About Privacy In Blockchain Networks (And Why Is It Hard To Achieve)?
An attempt to define what we mean by privacy, exploring how and why privacy in blockchain networks differs from web2, and why it's more difficult to achieve. We also provide a framework to evaluate different approaches for achieveing privacy in blockchain.

April 9, 2024
Will ZK Eat The Modular Stack?
Modularity enables faster experimentation along the tradeoff-frontier, wheras ZK provides stronger guarantees. While both of these are interesting to study on their own, this post explores the cross-over between the two.

October 5, 2023
Overview of Privacy Blockchains & Deep Dive Of Aleo
Programmable privacy in blockchains is an emergent theme. This post covers what privacy in blockchains entail, why most blockchains today are still transparent and more. We also provide a deepdive into Aleo - one of the pioneers of programmable privacy!
March 12, 2023
2022 Year In Review
If you’re reading this, you already know that 2022 was a tumultuous year for the blockchain industry, and we see little value in rehashing it. But you probably also agree with us that despite many challenges, there’s been a tremendous amount of progress.

May 31, 2022
Testing the Zcash Network
In early March of 2021, a small team from Equilibrium Labs applied for a grant to build a network test suite for Zcash nodes we named Ziggurat.

June 30, 2021
Connecting Rust and IPFS
A Rust implementation of the InterPlanetary FileSystem for high performance or resource constrained environments. Includes a blockstore, a libp2p integration which includes DHT contentdiscovery and pubsub support, and HTTP API bindings.
June 13, 2021
Rebranding Equilibrium
A look back at how we put together the Equilibrium 2.0 brand over four months in 2021 and found ourselves in brutalist digital zen gardens.
January 20, 2021
2021 Year In Review
It's been quite a year in the blockchain sphere. It's also been quite a year for Equilibrium and I thought I'd recap everything that has happened in the company with a "Year In Review" post.
